Many people feel safer with security cameras at home, knowing they have 24/7 monitoring to help deter intruders. Yet, these devices come with serious privacy risks and contain security vulnerabilities that bad actors can exploit.
Recent research found that feeds from more than 40,000 security cameras were openly accessible on the internet — meaning anyone could view and record the live footage. And even cameras that aren’t openly accessible are vulnerable to attacks from hackers, who can infiltrate home networks and exploit cybersecurity loopholes.
At the same time, these companies often collect more data than necessary, including precise location and payment details, making the companies prime targets for hackers.
In this article, we’ll uncover the hidden security and privacy dangers of home security cameras (including who has access to your devices), explore real-world hacking cases, and share practical tips to help you choose more secure cameras and strengthen your home’s digital defenses.
Hacking Risks: When Your Camera Is No Longer Protecting You
A 2022 US survey from U.S. News & World Report’s 360 Reviews found that 13% of respondents had been victims of security camera hacking incidents. Nearly half of respondents (49%) expressed concerns about hackers gaining access to their cameras, and 52% had taken preventative measures.
Real-world incidents show just how disturbing camera breaches can be. In 2025, a mother heard a strange voice from her child’s room, only to discover someone had hijacked her security camera and had been talking to her baby for days.
In another chilling case, two men managed to access dozens of Ring doorbell cameras by exploiting reused passwords and launched “swatting” attacks, a form of cybercrime in which a perpetrator fakes an emergency to get authorities to respond to the victim’s location. During the string of incidents in 2020, the attackers live-streamed the response, antagonizing police through the cameras.
In some of these incidents, the camera providers carry the blame — cameras that are designed for consumers to easily set up might skip important security protocols. And accidents may also happen. For example, in early 2024, after a service outage, 13,000 Wyze camera users momentarily saw other people’s video feeds. The company claimed it was a bug in a third-party service.
How Do Security Camera Attacks Happen and Are They Preventable?
Many security breaches stem from lax cybersecurity practices. One of the most common mistakes you can make is to use the default password that comes with your camera or create a weak password that’s easy for people to guess or crack through a brute force attack.
Another mistake is to ignore firmware or software updates with vital security patches. Even your home network can be a weak spot. An unencrypted Wi-Fi or a weak router password gives cybercriminals a backdoor into your camera.
Consumers also need to be aware of the common tactic of phishing. Attackers can trick you into revealing your account details by posing as the camera company in emails and text communications. This threat is becoming increasingly problematic with advances in AI, which allows bad actors to create convincing emails at scale in many languages.
Who Can Access or Watch Your Security Cameras?
Who, besides you as the owner, has access to a camera’s feed depends on your data location, the camera company’s policies, and data protection and privacy laws where you live. Generally, two other parties can access your footage, and they are:
1. Your Camera’s Service Provider
Security cameras have two storage solutions: local or cloud-based.
With local storage, your data is kept on a local device you control, such as a DVR, memory card, or local drive, and is not automatically sent to a cloud-based server. This gives you better privacy as the data stays on-premises (unless someone hacks into your home network or physically steals your storage device).
When you opt for cloud-based storage, on the other hand, your data is kept on the vendor’s servers. You can access your data from anywhere, but lose full control of it, as your recordings are now subject to the security and privacy protocols of the camera company.
2. Law enforcement agencies
When you store your videos in the cloud, law enforcement agencies can request access directly from the company without your permission.
In 2022, Amazon gave police access to video recordings 11 times, citing “emergency requests,” under a service in which law enforcement could request camera footage for Ring cameras. The company disabled this service in 2024 after public backlash. A CNET investigation in 2022 also found that Google shared users’ data with law enforcement without permission or a warrant.
If an officer asks you for video evidence without a warrant, you have the right to refuse in most jurisdictions. However, if your data is on the company’s cloud, you have little to no control.
Are AI-Powered Security Cameras Safe?
The latest home security cameras have AI features such as facial analysis, advanced motion detection, and behavior analytics. While these tools can enhance security, they also raise serious privacy concerns.
Facial recognition features analyze faces and create a detailed record of who visited and when. If this data is shared or hacked, it would compromise the security of you and your guests, especially those who never consented to being recorded or analyzed.
Furthermore, AI comes with the risk of algorithmic biases. Studies by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) found that facial recognition algorithms are less accurate when interpreting faces of certain races and ethnicities, increasing the risk of misidentification and profiling.
Behavior analytics go a step further by analyzing what people do, such as when and how often they leave the house or what their family is doing at home. Be aware that your service provider could share or monetize this data without your knowledge, based on their privacy policies. Read the terms of service carefully before buying a camera or enabling AI features in your device.
Choosing a Home Security Camera: Security and Privacy Features to Look For
Choosing the right camera is the first step toward better privacy and safety. When investing in a security camera, these are six essential security features to prioritize.

1. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
Encryption works by scrambling your data so that a unique key is required to access the original data. The encryption process can occur at different places, such as on your local network or a cloud server.
E2EE encrypts data locally on the camera before data is stored or transmitted to a server. This way, not even your camera provider can access your footage without the right key.
If you’re worried about security, having a camera supporting E2EE is a must. Older cameras tend to lack this feature, so consider upgrading if you’ve already set up a home surveillance system.
2. Data Location: Local vs. Cloud Storage
You’ll need to decide where to store your camera’s data, and each option has its own benefits and drawbacks.
With local storage, your data is on local drives and isn’t available online. This gives you sole control over who has access to your data and what is done with it, and also reduces your exposure to hackers.
However, you’ll have to set up your own storage network and buy the hardware, which could be expensive. You’ll also need to maintain and upgrade your local storage as needed, and could lose your data in the event of a fire, theft, or device malfunction.
With cloud storage, your data is in the cloud provided by the camera company or other cloud storage providers. These systems are often very user-friendly (you don’t have to set up, secure, or maintain local storage), and allow you to access your data at any time and from anywhere. And cloud providers typically provide backup services for your data.
However, your data is governed by the security and privacy rules of the camera company, as well as the laws in the state or country where the cloud servers are located. You’re also more exposed to breaches of, and technical mistakes by, the camera company.
3. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA is a security protocol that requires two forms of identification for access, adding another security layer to your data. For example, you’ll need a password and a passcode sent to your phone to log in to your camera app with 2FA enabled.
Using 2FA is one of the most effective ways to secure your home surveillance devices. If a malicious party manages to steal or guess your password, they won’t be able to access your cameras without that second form of identification.
4. Smart Home System Integration
Many people link their security cameras with smart home platforms such as Google Home, Apple HomeKit, or Alexa. By integrating your cameras into the smart home network, you can automate tasks, such as turning off bedroom cameras at night, setting up alerts for specific triggers, and combining alerts from all devices into one app.
However, device integration means shared network vulnerabilities. A camera that’s foolproof on its own might be compromised if it’s connected to an insecure smart home hub. For instance, your smart TV may have weak security settings, giving hackers an entry point into your entire home network.
When creating a smart home ecosystem, consider the security implications. Choose smart home systems from reputable vendors that offer features such as encryption and 2FA, and deliver regular security updates.
5. Customizable Camera Settings
The more customization your camera offers, the more options you have to strengthen your security and privacy. Look for customizable features like:
- Privacy modes: Turn off the camera remotely or set scheduled downtimes.
- Privacy zones: Block parts of the camera’s field of view, such as your bathroom.
- Audio controls: Disable audio recording to avoid hackers eavesdropping on your conversations in case of a breach.
6. Regular Software Updates
New cybercriminal tactics are constantly being developed, and new loopholes will appear as new technologies emerge. As a general rule, stay away from brands that rarely issue software updates. Most cameras have automatic updates to save you time, and it’s a good idea to check what was updated.
Before purchasing a camera, ask your family or friends for brand recommendations, and read online forums and reviews, paying particular attention to how often the software is updated.
How to Protect Your Camera from Cybersecurity Threats
Cyberattackers actively look for basic mistakes they can take advantage of. Some simple, practical steps can improve your home surveillance security and privacy, particularly with your camera, network, and cybersecurity habits.
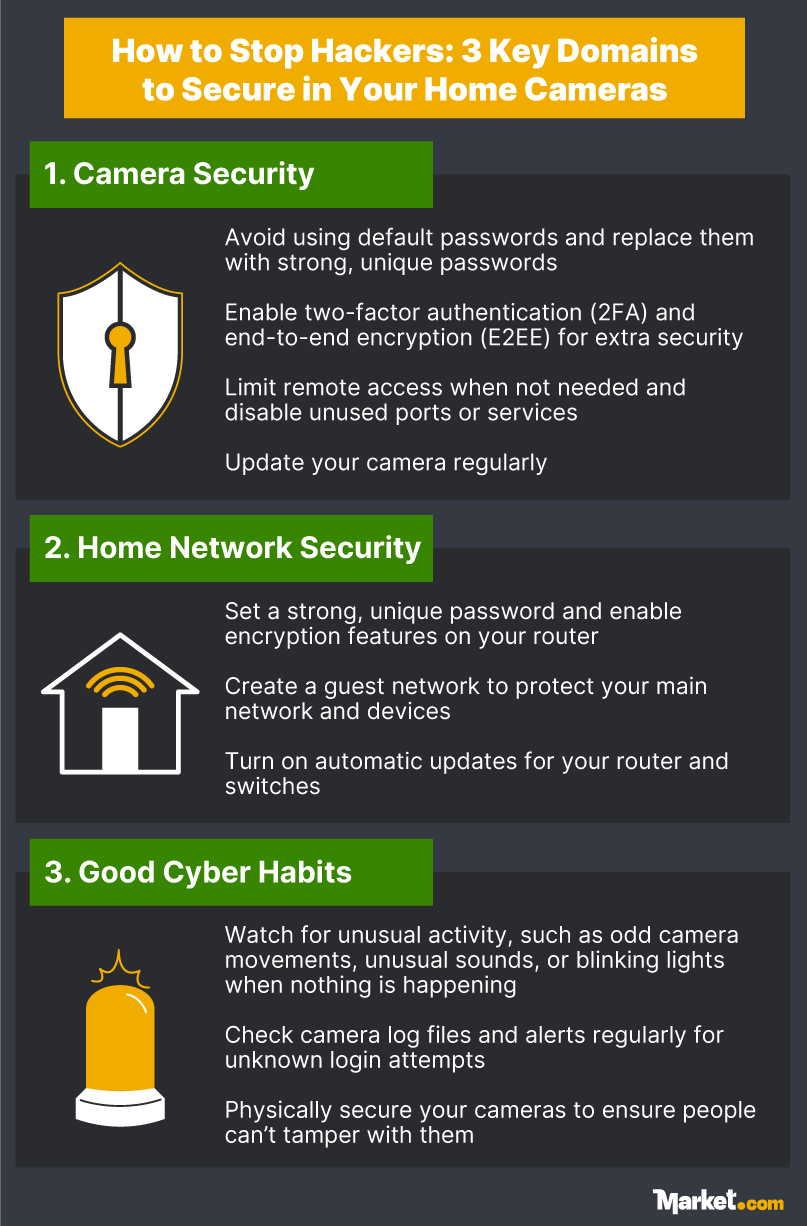
1. Secure Your Cameras
Take simple steps to secure cameras, including:
- Use strong passwords: Default passwords are among the easiest to crack. Create strong passwords, ideally around 16 characters long and a mix of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols. An alternative is to use four random words that are easy to remember.
- Create different passwords: Avoid using the same password across different devices and systems. A password manager can help by creating strong passwords for each application and storing them in an encrypted mode.
- Use 2FA and E2EE: Secure your devices with 2FA to stop attackers from cracking your password. Additionally, enable E2EE if your camera supports it to ensure your recordings are safe from prying eyes, including your service provider. This is particularly important if you store footage in the cloud.
- Turn off or limit remote access: Accessing your camera over the internet is convenient but carries risk. You can turn off remote access and only enable it when traveling to reduce the entry points for bad actors. Additionally, security experts recommend disabling unused ports or services on the camera to limit potential vulnerabilities hackers might exploit.
- Update your camera regularly: Don’t ignore or delay security updates. You can enable automatic updates or make it a habit to regularly check for them. Companies tend to phase out older camera models, and, ideally, you should upgrade your devices when they are no longer supported.
2. Strengthen Your Home Network
Your home network is another threat vector that needs to be secured. Simple, but important, steps include:
- Securing your Wi-Fi: Secure your entire home network. Use strong passwords for your routers and switches, changing them regularly for extra security. Plus, switch on encryption features if your router supports it.
- Setting up a guest network: Segmenting your home network allows you to isolate and contain attacks quickly to minimize damage. Creating a separate Wi-Fi network for guests means hackers can’t reach your main devices, such as security cameras and mobile phones, in an attack.
- Updating your network devices: Your routers and switches require regular security updates. An outdated router is an easy target, so remember to check for updates or enable automatic firmware updates.
3. Establish Good Cybersecurity Routines
Your cyber hygiene — the habits you develop around your devices and systems — is an important element in your security. Create routines that include:
- Monitoring for unusual camera activities: There are tell-tale signs that someone is taking control of your cameras, including unusual blinking lights from your camera (some camera models flash when someone is viewing the feed), camera movements, and strange sounds when nothing is happening in your home. Power off the camera and investigate immediately if you notice these signs.
- Checking log files and notifications: Establish a routine of verifying log files and checking notifications for anything out of the ordinary. If you discover login times and device names that don’t make sense, this could be a sign that someone tried to hijack your cameras.
- Physically securing your devices: Digital security is only half of the equation. You’ll also need to ensure your devices are physically secure. Check regularly that your cameras haven’t been tampered with. If you’re using other devices as part of your home surveillance network, keep them safe too. Cyberattacks can happen when people lose their phones or tablets, giving cybercriminals easy access to their cameras.
What to Do If You Suspect a Cyberattack On Your Camera?
If you believe your camera has been compromised, stay calm and act quickly to stop further attacks. Here’s a checklist to help you respond:
- Power the camera(s) off
- Remove it from the network
- Look for suspicious login attempts to the network or the camera
- Change the passwords on your home Wi-Fi and cameras
- Scan the device and network for malware
- Disable remote monitoring
- Run a factory reset on the camera if needed
- Ensure you have the latest firmware and software updates
- Lodge a case with customer support
- Report to the police if you have enough evidence of intrusion
- Monitor for ongoing unusual activity
- Consider upgrading your camera to one with more security features.
Focusing on your camera setup, network, and security habits can significantly reduce your exposure to cyberattacks. Home surveillance systems are an important layer of protection — but only if you take steps to protect them.
The Bottom Line
Security cameras increase your home’s safety, but can become a threat vector if not properly secured. The good news is that most attacks are preventable. Careless setup and sloppy security measures are the main reasons you’re more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Your first line of defense is picking the right camera. Choose cameras with robust security features like E2EE, 2FA, customizable security settings, and regular firmware updates. The data storage location also matters. Local storage gives you more control but less flexibility, while cloud storage is more convenient but comes at the expense of less control over your data.
You’ll also need to secure your home network by changing default passwords, using strong encryption, and updating your router. Likewise, maintaining good cybersecurity routines through regular monitoring and security log checks will strengthen your home security.
Most importantly, stay vigilant. Monitor for unusual activities and be mindful of who has access to your system, including well-intentioned third parties. With proactive measures, you can enjoy the benefits home cameras bring without compromising your personal life.


